Best Way to Encrypted Data Transfer
This article delves into the significance of encrypted data transfer in the digital world, covering how it works, its applications, and best practices for securing sensitive information. It highlights AnyViewer as an optimal choice for maintaining data security.
Introduction
In an era dominated by technology, where information flows freely across the internet, the security of our data has never been more critical. From personal conversations to sensitive business transactions, the exchange of information is susceptible to various threats, including hacking, phishing, and data breaches. This concern has placed encrypted data transfer at the forefront of data security discussions. So, what does this term really mean, and why should you care about it? How to securely transfer large files? Let’s unpack the intricacies of encrypted data transfer and explore its essential role in our digital lives.
What is Encrypted Data Transfer?
At its core, encrypted data transfer is a method of securing information as it moves between two or more parties. It involves encoding the data in such a way that only authorized users can access it. This is accomplished through the use of encryption algorithms, which transform readable data (known as plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext). This transformation ensures that even if someone intercepts the data during transmission, they cannot comprehend it without the appropriate decryption key.
To visualize this, think about sending a postcard with your personal information written on it. Anyone who intercepts that postcard can read its contents. Now, imagine sealing that information inside an envelope before mailing it—this is akin to encryption. The data is protected, and only the intended recipient can open the envelope to read what’s inside.
Importance of Encrypted Data Transfer
So, why is encrypted data transfer crucial? Well, let’s consider this: every time you log into your bank account, share personal information, or even send a simple email, you’re trusting that your data will remain confidential. Without encryption, that trust is misplaced. Here are a few reasons why encrypted data transfer is vital:
- Protection Against Cyber Threats: Cyberattacks are increasingly sophisticated. Without encryption, sensitive data like credit card numbers, social security numbers, and passwords are vulnerable to theft. Hackers often deploy techniques such as man-in-the-middle attacks, where they intercept and alter communications between two parties. Encryption acts as a formidable barrier, making it much harder for attackers to access sensitive information.
- Regulatory Compliance: Numerous industries must adhere to strict regulations concerning data protection. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandate stringent measures for handling sensitive data. Encryption helps organizations comply with these regulations, protecting them from hefty fines and legal repercussions.
- Maintaining Customer Trust: When businesses prioritize data security, it builds trust with customers. In an era where data breaches are alarmingly common, encryption is a key factor in demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding personal information. Companies that can assure their customers that their data is encrypted are more likely to retain customer loyalty.
Why Do We Need Encrypted Data Transfer?
Protecting Sensitive Information
In today’s digital landscape, sensitive information is everywhere—from social security numbers and credit card details to corporate trade secrets. The need for protection has become paramount. Encrypted data transfer serves as a shield, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and is not accessible to unauthorized parties.
For instance, consider a healthcare provider sending patient records to a specialist. Without encryption, this information could be intercepted and misused. By using data transfer encryption, the healthcare provider can ensure that the records remain private, thereby upholding patient confidentiality.
Compliance with Regulations
Various industries face strict regulations that require them to protect sensitive information. For example, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States mandates healthcare organizations to secure patient data. Similarly, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) enforces strict data protection rules in Europe. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, making encrypted transfer data not just a best practice but a legal requirement for many organizations.
How Encrypted Data Transfer Works
Now that we understand what encrypted data transfer is and why it matters, let’s delve into how it works. The process of encryption involves algorithms that transform plaintext into ciphertext. Here’s an easy-to-follow outline of the steps:
- Data Input: The original data is prepared for encryption. This could be anything from a simple text message to a complex database file.
- Encryption Algorithm: An encryption algorithm processes the plaintext and scrambles it into ciphertext using a specific key. This key is a piece of information that determines how the data will be encrypted and later decrypted.
- Ciphertext Output: The scrambled data is then sent across the network. At this stage, even if a malicious actor intercepts the data, they will see only an incomprehensible string of characters.
- Decryption: Upon receiving the ciphertext, the intended recipient uses a corresponding decryption key to convert the data back into its original, readable format. Only someone with the correct key can do this, ensuring the information’s confidentiality.
There are two primary types of encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption: Using the same key, this method encrypts and decrypts data. While it is efficient, the challenge lies in securely sharing the key with the recipient.
- Asymmetric Encryption: This method uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. While the private key needs to be kept private, the public key can be freely shared. This approach enhances security but can be slower than symmetric encryption.
Methods of Encrypted Data Transfer
There are several methods and protocols used for encrypted data transfer. A handful of the more prevalent ones will be examined:
TLS and SSL Protocols
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are the backbone of secure internet communications. These protocols encrypt the data sent between your computer and the server, making it difficult for anyone to eavesdrop or tamper with the information.
When you visit a website that starts with “https://,” you’re utilizing TLS/SSL to ensure safe browsing. The ‘s’ at the end of ‘http’ stands for ‘secure,’ indicating that the website encrypts data exchanged between your browser and the server. This means that even if someone intercepts the data while it’s being transferred, they will only see encrypted gibberish.
VPNs and Encrypted Data
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure way to connect to the internet by encrypting all data transmitted between your device and the VPN server. This adds an additional layer of security, making it incredibly challenging for anyone to track your online activities.
When using a VPN, your internet traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel, preventing third parties—including hackers, internet service providers, and government agencies—from monitoring your online behavior. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are notoriously insecure. By connecting through a VPN, users can surf the web privately and securely, effectively masking their IP addresses and locations.
Challenges in Encrypted Data Transfer
Despite its advantages, data transfer encryption isn’t without challenges.
Misconceptions About Encrypted Data Transfer
One frequent fallacy is that encryption renders data entirely secure. While encryption is a powerful tool, it isn’t foolproof. Factors such as poor key management, weak encryption methods, and human error can lead to vulnerabilities. For example, if a decryption key is shared insecurely or stored improperly, it can be easily accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Additionally, not all encryption algorithms are created equal. Some older methods may no longer provide adequate security against modern threats. Organizations must continually evaluate their encryption strategies to ensure they remain effective in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Best Practices for Ensuring Encrypted Data Transfer
While understanding encrypted data transfer is crucial, implementing best practices can significantly enhance your security. Here are some effective strategies:
- Use Strong Passwords: Always protect your encrypted data with strong, unique passwords. Steer clear of easily guessable information such as birthdays or common words. It's a good idea to use a password manager to create and store strong, complex passwords.
- Regular Updates: Ensure your encryption software and protocols are up-to-date to guard against vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity threats evolve rapidly, and staying current with updates ensures that you’re protected against known exploits.
- Educate Users: If you’re part of an organization, make sure everyone understands the importance of data encryption and best practices. Regular training sessions can help employees recognize phishing attempts and other tactics that could compromise data security.
The Role of VPNs in Encrypted Data Transfer
VPNs are essential tools for secure online communications. They create a private network from a public internet connection, encrypting all data that passes through it. This means that your online activities—such as browsing, streaming, or file sharing—remain private, even on unsecured networks like public Wi-Fi.
Using a VPN is like having a personal bodyguard for your internet activities. When you connect to a VPN, your data is encrypted, and your IP address is concealed. This added layer of anonymity makes it significantly harder for hackers to track your online activities or intercept your data.
For example, if you're working remotely from a coffee shop and using their Wi-Fi, a hacker could easily access your unencrypted data. However, with a VPN, your information remains secure, protecting you from potential threats.
Future Trends in Encrypted Data Transfer
As technology evolves, so too do the methods and tools for encryption. Here are a few emerging trends to watch for:
- Quantum Encryption: With the rise of quantum computing, traditional encryption methods may become vulnerable. Quantum encryption, utilizing principles of quantum mechanics, offers a way to secure data that is theoretically unbreakable.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This cutting-edge technology allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it first. This means that sensitive data can be processed securely, preserving privacy while still allowing for data analysis.
- Increased Regulation: As concerns over data privacy grow, expect stricter regulations around data protection. Organizations will increasingly be required to adopt encrypted transfer data practices to ensure compliance with laws like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Integration with AI: Artificial intelligence will play a role in enhancing encryption technologies. AI can help identify patterns of data breaches and improve the speed and efficiency of encryption processes.
Best Way to Encrypted Data Transfer
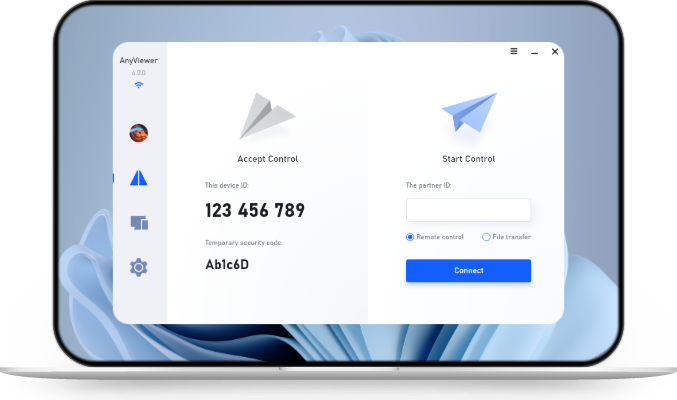
AnyViewer stands out as one of the most secure and reliable remote desktop software solutions on the market, offering not only smooth remote access but also a powerful file transfer feature designed for encrypted data transfer. What sets AnyViewer apart is its use of advanced encryption protocols, such as end-to-end encryption and two-factor authentication, which safeguard every connection and file transfer. Whether you’re managing sensitive corporate data or simply sharing personal files between devices, AnyViewer ensures that your information remains private, secure, and protected from cyber threats or unauthorized access.
Additionally, the platform is incredibly user-friendly, with a clean interface that makes remote access and file sharing straightforward, even for non-technical users. Speed is another major advantage; file transfers happen swiftly without compromising security, making AnyViewer perfect for professionals who need to exchange large files efficiently. It’s compatible with multiple devices, including Windows and mobile platforms, allowing users to stay connected and in control from anywhere.
For businesses, IT professionals, and individuals who prioritize both security and efficiency, AnyViewer is an essential tool. Its combination of secure remote access, encrypted file transfer, and ease of use makes it a top choice for anyone needing a trustworthy remote desktop solution.
Step 1. Please download and install AnyViewer on both your local and remote devices first. Open the app on both sides. In the "Log in" section, click "Sign up" and create your account by entering the necessary details.
Step 2. Log in to the same account on your remote device. Once logged in, your remote device will automatically sync with your account.
Step 3. On your local computer, choose the remote device to which you want to transfer files. Click the "File transfer" option.
To enable unattended remote access, select the "One-click control" option, which lets you connect to a remote computer and use it as if you were physically present. Once connected, you can transfer files by clicking the "File" button in the top menu.
For a faster, simpler transfer, you can also drag and drop files directly from your local device to the remote computer.
Step 4. The File Transfer window will appear. Choose the files you want to send and either click the arrows or double-click to start the transfer.
- ★Tips: If you need to transfer larger files, consider upgrading to AnyViewer's Professional or Enterprise plan. Here are the key benefits you can expect:
- Faster Transfers: Enjoy speeds of up to 10 MB/s for faster file transfers.
- Concurrent Transfers: Manage up to five file transfers simultaneously.
- Unlimited Transfers: Send unlimited files in a single session with no restrictions.
- Large File Support: Transfer files up to 1 TB in size, ideal for handling large projects.
- ...
Conclusion
In conclusion, encrypted data transfer is essential in today’s digital landscape for protecting sensitive information and ensuring secure communications. Whether it's safeguarding personal details or adhering to industry regulations, encryption plays a vital role in defending against cyber threats. Implementing best practices like using strong encryption protocols and tools is crucial. AnyViewer, with its robust encryption, secure file transfer, and user-friendly interface, is an excellent solution for ensuring your data remains private and protected. With its advanced features, AnyViewer offers an efficient and reliable method for secure data transfer, making it a top choice for businesses and individuals alike.